Singapore’s HealthTech agency, Synapxe has partnered with the country's Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) to develop a pilot project to onboard artificial intelligence (AI) powered software in its healthcare ecosystem for accurate CT scan interpretations.
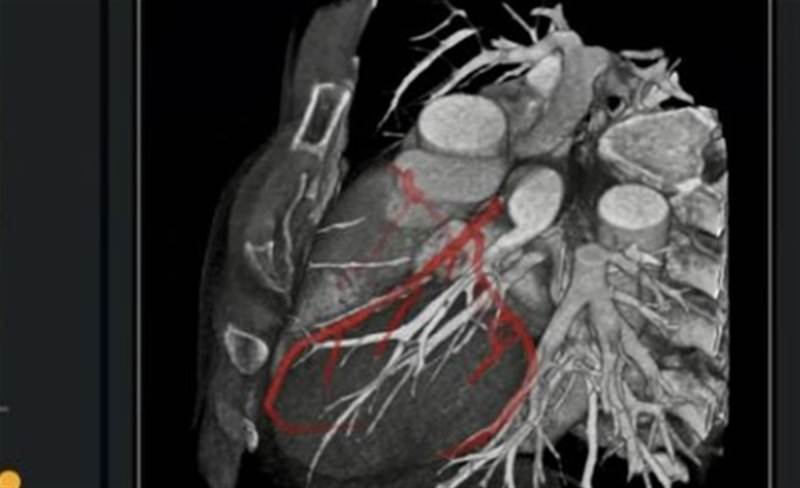
APOLLO is an AI-enabled CT scan interpretation software co-developed by A*STAR together with its partners, Duke-NUS Medical School, Nanyang Technological University (NTU), National Heart Centre Singapore (NHCS), National University Hospital (NUH) and Tan Tock Seng Hospital (TTSH).
It automates the analysis of medical images with greater speed and accuracy, enabling more efficient triaging of patients with different care needs.
It also helps radiologists to "efficiently" generate radiology reports, improving the quality of clinician diagnoses and reducing unnecessary tests and procedures.
With the APOLLO software platform, clinicians can receive the interpretation of resultant CT scans in less than 10 minutes, Synapxe said in a release.
A*STAR Biomedical Research Council's assistant chief executive Prof Tan Sze Wee said the agency is working closely with clinical partners to develop impactful healthcare solutions.
The partnership with Synapxe aims to address common challenges in healthcare administration, identify emerging technologies, and co-create scalable solutions for deployment into the healthcare system, he added.
The key initiative is to onboard APOLLO onto AI medical imaging platform AimSG for rapid development, testing, and deployment of AI imaging models.
Improving investigation efficiency
Singapore accounted for 31.4 percent of deaths due to cardiovascular diseases in 2022. It is the leading cause of death globally, taking an estimated 17.9 million lives each year.
While international guidelines recommend computed tomography coronary angiography (CTCA) as the first-line investigative tool for coronary artery disease (CAD), interpretation of the resultant CT scans is time-consuming, generally requiring one to two hours for standard cases and even up to four hours in complex cases for clinicians.
Synapxe said that the platform utilises AI algorithms and patented post-processing technologies to deliver precise measurements and assessments for coronary calcium scores, epicardial adipose tissue (EAT), stenosis and plaque, which together with the CTCA interpretation, represents a comprehensive CAD evaluation.
With improved efficiency and comprehensiveness of the platform, Prof Tan said hospitals would be able to advise patients about their CAD risk; allowing them to take preventive measures and seek appropriate treatment.
Through the new deal with Synapxe, he said the agency aims to "spur translation of these solutions to public healthcare institutions to benefit patients, better support workers, and improve healthcare delivery."